- Global - 全局对象
- Automator - 自动化
- AutoJs6 - 本体应用
- App - 通用应用
- Color - 颜色
- Image - 图像
- OCR - 光学字符识别
- Barcode - 条码
- QR Code - 二维码
- Keys - 按键
- Device - 设备
- Storage - 储存
- File - 文件
- Engine - 引擎
- Task - 任务
- Module - 模块
- Plugins - 插件
- Toast - 消息浮动框
- Notice - 消息通知
- Console - 控制台
- Shell
- Shizuku
- Media - 多媒体
- Sensor - 传感器
- Recorder - 记录器
- Timer - 定时器
- Thread - 线程
- Continuation - 协程
- Event - 事件监听
- Dialog - 对话框
- Floaty - 悬浮窗
- Canvas - 画布
- UI - 用户界面
- Web - 万维网
- HTTP
- Base64
- Crypto - 密文
- OpenCC - 中文转换
- Internationalization - 国际化
- Standardization - 标准化
- E4X
- UiSelector - 选择器
- UiObject - 控件节点
- UiObjectCollection - 控件集合
- UiObjectActions - 控件节点行为
- WebSocket
- EventEmitter - 事件发射器
- ImageWrapper - 包装图像类
- App - 应用枚举类
- Color - 颜色类
- Version - 版本工具类
- Polyfill - 代码填泥
- Arrayx - Array 扩展
- Numberx - Number 扩展
- Mathx - Math 扩展
- Glossaries - 术语
- HttpHeader - HTTP 标头
- HttpRequestMethods - HTTP 请求方法
- MimeType - MIME 类型
- NotificationChannel - 通知渠道
- Data Types - 数据类型
- Omnipotent Types - 全能类型
- Storage - 存储类
- AndroidBundle
- AndroidRect
- CryptoCipherOptions
- CryptoKey
- CryptoKeyPair
- ConsoleBuildOptions
- HttpRequestBuilderOptions
- HttpRequestHeaders
- HttpResponseBody
- HttpResponseHeaders
- HttpResponse
- InjectableWebClient
- InjectableWebView
- NoticeOptions
- NoticeChannelOptions
- NoticePresetConfiguration
- NoticeBuilder
- Okhttp3HttpUrl
- OcrOptions
- Okhttp3Request
- OpenCVPoint
- OpenCVRect
- OpenCVSize
- OpenCCConversion
AutoJs6 文档 - 6.6.4
目录
- 数据类型 (Data Types)
- 操作符
- 操纵泛型
- 自定义类型
- JavaArray
- JavaArrayList
- NumberString
- ComparisonOperatorString
- ScreenMetricNumberX
- ScreenMetricNumberY
- ScriptExecuteActivity
- DetectCompass
- DetectResult
- DetectCallback
- PickupSelector
- PickupResult
- UiObjectInvokable
- RootMode
- ColorHex
- ColorInt
- ColorName
- ColorComponent
- ColorComponents
- ColorDetectionAlgorithm
- Range
- IntRange
- StandardCharset
- ExtendModulesNames
- ActivityShortForm
- BroadcastShortForm
- OcrModeName
- OcrResult
- ThemeColor
- JsByteArray
- ByteArray
- CryptoDigestAlgorithm
- CryptoKeyPairGeneratorAlgorithm
- CryptoDigestOptions
- CryptoCipherTransformation
- Storage
- AndroidBundle
- AndroidRect
- CryptoCipherOptions
- ConsoleBuildOptions
- HttpRequestBuilderOptions
- HttpRequestHeaders
- HttpResponseBody
- HttpResponseHeaders
- HttpResponse
- InjectableWebClient
- InjectableWebView
- NoticeOptions
- NoticeChannelOptions
- NoticePresetConfiguration
- NoticeBuilder
- Okhttp3HttpUrl
- OcrOptions
- Okhttp3Request
- OpenCVPoint
- OpenCVRect
- OpenCVSize
- OpenCCConversion
数据类型 (Data Types)#
此章节待补充或完善...
Marked by SuperMonster003 on Feb 22, 2023.
数据类型是用来约束数据的解释.
本章节的数据类型包括 [ number / void / any / object / 泛型 / 交叉类型 ] 等.
注: 此章节的类型概念 与 JavaScript 数据类型 (如 基本类型) 以及 TypeScript 数据类型 (如 基础类型) 在概念上可能存在出入, 因此仅适用于对文档内容的辅助理解, 不适用于严格的概念参考.
Boolean#
布尔类型.
foo(bar)
- bar { boolean }
foo(true); /* 符合预期. */
foo(false); /* 符合预期. */
foo(3); /* 不符合预期. */
需留意 JavaScript 的短路特性:
/* 符合预期, 相当于 foo(false). */
foo(3 > 4);
/* 不符合预期, 相当于 foo("hello"). */
foo(3 > 4 || "hello");
/* 符合预期, 相当于 foo(false). */
foo(3 > 4 && "hello");
/* 不符合预期, 相当于 foo("hello"). */
foo(3 > 2 && "hello");
Number#
数字类型.
常用以下表示方法:
3- 整数+3- 整数- 结果与 3 相同, 通常仅用于强调正负性
- 这里的 "+" 并非符号, 而是一元运算符
-3- 负数3.1- 小数- JS 使用 IEEE 754 双精度版本存储数字
- 参阅: 0.1 + 0.2 !== 0.3
3.0- 整数- 结果与 3 相同, JS 没有 Double 等类型
.1- 小数, 省略前导 0, 相当于 0.12e3- 科学计数法, 相当于 2 × 10^3, 即 2000- 符号 e 表示 10 的幂, e 前后的数字分别称为有效数和幂次
- 有效数可以为整数或小数字面量:
1e2,3.1e2,-9e2,0e2,.1e2均合法
- 幂次只能为整数字面量:
1e2,1e-2均合法
- e 的前后不能有变量或括号等符号:
let num = 3;nume2,(num)e2,(3)e(2),3e(num)均不合法
0x23- 十六进制0b101- 二进制0o307- 八进制NaN- 特殊数值- 参阅: NaN
Infinity- 无穷大-Infinity- 负无穷大Number.XXX- Number 对象上的常量Math.XXX- Math 对象上的常量- 如 Math.PI, Math.SQRT2, Math.LN2 等
foo(bar)
- bar { number }
foo(3); /* 符合预期. */
foo(3.3); /* 符合预期. */
foo(3e3); /* 符合预期. */
foo(NaN); /* 符合预期. */
JavaScript 的所有数字都是浮点数, 因此 number 类型对 Double, Float, Long, Integer, Short 等均不作区分.
3.0 === 3; // true
typeof new java.lang.Double(5.23).doubleValue(); // "number"
注: 如需表示一个很大的数 (超过
2^53 - 1), 需要用 BigInt 表示.
文档中通常不会出现bigint类型的数据, 包括number | bigint这样的 联合类型 数据.
String#
字符串类型.
常用以下表示方法:
"hello"- 成对双引号 (")'hello'- 成对单引号 (')`hello`- 成对反引号 (`)- 参阅: 模板字符串
转义字符- 如
\n,\r,\uXXXX,\xXX等 - 参阅: 转义字符
- 如
foo(bar)
- bar { string }
foo("3"); /* 符合预期. */
foo('3.3'); /* 符合预期. */
foo(`3e3 equals to ${3000}`); /* 符合预期. */
foo(NaN.toString()); /* 符合预期. */
Array#
数组类型.
后缀 "[]" 代表数组类型.
如 number[] 代表一个数组, 其中的元素全部为 number 类型, 且元素数量不限 (包括 0, 即空数组).
注:
number[]与[number]不同, 后者表示 元组类型.
注: 使用
Array<T>这样的 泛型 表示法也可代表数组类型, 但文档通常只采用后缀表示法.
foo(bar)
- bar { string[] }
foo([ "3" ]); /* 符合预期. */
foo([ 3 ]); /* 不符合预期. */
foo([ "3", 3 ]); /* 不符合预期. */
foo([]); /* 符合预期. */
Tuple#
元组类型.
元组类型严格限制数组的对应类型及元素数量.
如 [ number, number, string, number ] 有如下限制:
- - 数组有且必有 4 个元素;
- - 元素类型依次为 number, number, string, number.
注: 需额外注意元组类型与 JSDoc 表示数组方法的异同.
另外 JavaScript 中没有元组的概念.
foo(bar)
foo([ "3" ]); /* 不符合预期. */
foo([ 3 ]); /* 不符合预期. */
foo([ "3", 3 ]); /* 符合预期. */
foo([]); /* 不符合预期. */
Function#
函数类型.
文档采用 箭头函数 表示一个函数参数.
foo(bar)
上述 方法签名 中, bar 为函数参数, 该函数是一个无参函数且返回值为 number 类型.
foo(Math.random()); /* 不符合预期. */
foo(function () {
return Math.random();
}); /* 符合预期. */
foo(function () {
return 'hello';
}); /* 不符合预期. */
foo(bar)
上述 方法签名 中, bar 为函数参数, 该函数包含两个参函数且返回值为 string 类型.
/* 参数 a 为 string 类型, b 为 any 类型. */
foo(function (a, b) {
return a + String(b); /* 字符串拼接. */
}); /* 符合预期. */
RegExp#
正则表达式类型.
foo(bar)
- bar { RegExp }
上述 方法签名 中, bar 为正则表达式参数, 是 JavaScript 标准 RegExp 类型:
字面量
foo(/hello.+world?/)RegExp 构造器
new RegExp('hello.+world?')
参阅: MDN
Any#
任意类型.
类型 any 能够兼容所有类型.
foo(bar)
- bar { any }
foo(3); /* 符合预期. */
foo([]); /* 符合预期. */
foo({}); /* 符合预期. */
foo(null); /* 符合预期. */
尽管 any 可以兼容所有类型, 但仍需提供一个具体的类型, 不能省略:
foo(); /* 不符合预期. */
foo(undefined); /* 符合预期. */
Void#
此类型用于表示一个函数没有返回值.
作为函数体返回值#
foo(bar)
Void 作为 foo 函数体的返回值类型, 表示 foo 函数没有返回值:
function foo() {
console.log("hello");
} /* 符合预期. */
function foo() {
return "hello";
} /* 不符合预期. */
作为参数返回值#
foo(bar)
上述 方法签名 中, bar 为函数参数,
void 并非表示要求其返回值为 void,
它表示 bar 返回的所有值均被忽略 (即不被关心).
let arr = [];
foo(() => arr.push(Math.random())); /* 符合预期. */
console.log(arr);
Void 与 Undefined#
foo(bar)
在 JavaScript 中, 没有 return 语句的函数将默认返回 undefined.
因此对于函数体, 返回值为 void 相当于 undefined:
foo(() => {
return;
}) /* 符合预期. */;
foo(() => {
return undefined;
}) /* 符合预期. */;
foo(() => {
// Empty body.
}) /* 符合预期. */;
foo(() => {
return 3;
}) /* 不符合预期. */;
foo(bar, baz)
对于函数参数, 返回值 void 与 返回值 undefined 意义不同.
void 表示返回的所有值均被忽略 (参阅 作为参数返回值),
而 undefined 表示返回值必须为 undefined 类型.
foo(
/* bar = */ () => {
return;
}, /* 符合预期. */
/* baz = */ () => {
return;
}, /* 符合预期. */
);
foo(
/* bar = */ () => {
return undefined;
}, /* 符合预期. */
/* baz = */ () => {
return undefined;
}, /* 符合预期. */
);
foo(
/* bar = */ () => {
// Empty body.
}, /* 符合预期. */
/* baz = */ () => {
// Empty body.
}, /* 符合预期. */
);
foo(
/* bar = */ () => {
return 3;
}, /* 符合预期. */
/* baz = */ () => {
return 3;
}, /* 不符合预期. */
);
注: 上述方法签名如果将 void 替换为 any, 就 bar 参数是否符合预期方面而言, 效果是相同的.
然而两者在语义上有明确不同, void 表示不关心 bar 的返回值, 而 any 表示任意返回值类型均可接受.
在设计自定义 API 或设计 TS 声明文件时, 上述区分将显得尤为重要.
Never#
Object#
字面量对象类型#
{ { a: number }}
Generic#
Null#
参阅: MDN #术语 / MDN #操作符 / MDN #Nullish
Undefined#
// device.vibrate(text: string, delay?: number): void
typeof device.vibrate("hello") === "undefined"; // true
RegExPattern#
正则表达式模式类型.
通常只在 操纵泛型 中使用.
foo(bar)
foo("1"); /* 符合预期. */
foo("123"); /* 符合预期. */
foo("hello"); /* 不符合预期. */
foo("1e3"); /* 不符合预期. */
foo("1.3"); /* 不符合预期. */
联合类型#
操作符#
in#
keyof#
typeof#
extends#
index#
condition#
readonly#
操纵泛型#
例如 Array
Uppercase#
Uppercase<T>: string
通常用于输出转换.
接受 string 类型并生成所有字母大写的同类型数据.
Lowercase#
Lowercase<T>: string
通常用于输出转换.
接受 string 类型并生成所有字母小写的同类型数据.
Capitalize#
Capitalize<T>: string
通常用于输出转换.
接受 string 类型并生成首字母大写的同类型数据.
IgnoreCase#
IgnoreCase<T extends string>: T
通常用于参数值的输入转换.
接受 string 类型并生成忽略大小写的同类型数据.
例如, 对于 IgnoreCase<"webUrl">, 以下数据均符合预期:
[ "webUrl", "WEBURL", "WebUrl", "WEBurl" ];
但不能在字符串前后或内部插入其他字符,
如 [ "WEB_URL" / "web-url" / "#WebUrl" ] 等.
Pattern#
Pattern<T extends RegExPattern>: string
通常用于输入检查.
接受 正则表达式字面量 并生成通过测试的 string 类型数据.
Pattern 的泛型通配符 T 在文档中也称作 字符串模式.
foo(bar)
- bar { Pattern</^https?:/> }
foo("http is an abbreviation."); /* 不符合预期. */
foo("https://xxx"); /* 符合预期. */
foo("ftp://xxx"); /* 不符合预期. */
支持 标记参数:
foo(bar)
- bar { Pattern</^h...[oy]/i> }
foo("Happy"); /* 符合预期. */
foo("hello"); /* 符合预期. */
foo("Halloween"); /* 符合预期. */
foo("history"); /* 符合预期. */
foo("heroes"); /* 不符合预期. */
为便于理解或重复引用, 有些 Pattern 类型会被重新定义为自定义类型, 如 NumberString.
注: 目前 (2022/08) 在 JSDoc 及 TypeScript 中,
均不存在使用正则表达式字面量检查字符串的类型检查 (参阅 StackOverflow),
上述 Pattern 类型仅适用于对文档内容的辅助理解.
AnyBut#
AnyBut<T>
任意类型但排除 T.
foo(bar)
上述示例的 bar 参数接受除 number 外的任意类型.
自定义类型#
JavaArray#
Java Array (Java 数组).
let javaArr = java.lang.reflect.Array
.newInstance(java.lang.Float.TYPE, 3);
console.log(util.isJavaArray(javaArr)); // true
console.log(Array.isArray(javaArr)); // false
Java 数组可使用 JavaScript 数组的属性及方法:
let javaArr = java.lang.reflect.Array
.newInstance(java.lang.Float.TYPE, 3);
console.log(javaArr.length); // 3
console.log(javaArr.slice === Array.prototype.slice); // true
Array.isArray(javaArr.slice(0)); // true
Java 数组一旦被初始化, 长度将不可改变, [ 改变长度 / 越界赋值 ] 均会失败且抛出异常:
let javaArr = java.lang.reflect.Array
.newInstance(java.lang.Float.TYPE, 3);
/* 静默失败. */
javaArr.length = 20;
console.log(javaArr.length); // 3
/* push 或 unshift 导致越界抛出异常. */
javaArr.push(9); /* Error. */
javaArr.unshift(9); /* Error. */
/* pop 或 shift 不抛出异常但不改变数组长度. */
javaArr.pop();
console.log(javaArr.length); // 3
javaArr.shift();
console.log(javaArr.length); // 3
/* 越界访问不抛出异常, 会返回 undefined. */
console.log(javaArr[9]); // undefined
/* 越界赋值将抛出异常. */
javaArr[9] = 10; /* Error. */
Java 数组中的元素将隐式转换为指定的类型, 同时此类型也会被转换为 JavaScript 类型, 如 Java 的 Integer 等均转换为 Number:
let javaArr = java.lang.reflect.Array
.newInstance(java.lang.Integer.TYPE, 3);
console.log(javaArr.join()); // '0,0,0'
/* Number('1a') -> NaN */
javaArr[0] = '1a';
console.log(javaArr[0]); // NaN
/* Number('2.2') -> 2.2 $ JS */
/* java.lang.Integer(2.2 $ JS) -> 2 $ Java */
/* Number(2 $ Java) -> 2 $ JS */
javaArr[2] = '2.2';
console.log(javaArr[0]); // 2
/* 0xFF $ Hexadecimal == 255 $ Decimal / JS */
/* java.lang.Integer(255 $ JS) -> 255 $ Java */
/* Number(255 $ Java) -> 255 $ JS */
javaArr[0] = 0xFF;
console.log(javaArr[0]); // 255
参阅: Oracle Docs
JavaArrayList#
Java ArrayList (Java 数组列表).
与 Java Array 不同的是, ArrayList 创建的数组可调整大小:
let arrList = new java.util.ArrayList();
arrList.add(10);
arrList.add('20');
arrList.add([ '30' ]);
arrList.add(/40/g);
console.log(arrList.length); // 4
arrList.forEach((o) => {
// 10 (Number)
// 20 (String)
// 30 (Array)
// /40/g (RegExp)
console.log(`${o} (${species(o)})`);
});
arrList.addAll(arrList);
console.log(arrList.length); // 8
arrList.clear();
console.log(arrList.length); // 0
参阅: Oracle Docs
NumberString#
数字字符串.
字符串模式: /[+-]?(\d+(\.\d+)?(e\d+)?)/.
"12";
"-5";
"1.5";
"1.5e3";
ComparisonOperatorString#
比较操作符字符串.
字符串模式: /<=?|>=?|=/.
">";
">=";
"<";
"<=";
"="; /* 对应全等操作符 "===" . */
ScreenMetricNumberX#
屏幕横向度量值.
表示方式:
- 数字 { X >= 1 或 X < -1 } - 横向屏幕宽度值
- 数字 { X > -1 且 X < 1 } - 横向屏幕宽度值的百分比
- 数字 { X == -1 } - 横向屏幕宽度值本身 (代指值)
例如, 对于下面的参数:
bottom { ScreenMetricNumberX }
bottom 赋值为 50, 表示 X 坐标为 50.
bottom 赋值为 -80, 表示 X 坐标为 -80.
bottom 赋值为 0.5, 表示 X 坐标为 50% 横向屏幕宽度, 即 0.5 * device.width.
bottom 赋值为 -0.1, 表示 X 坐标为 -10% 横向屏幕宽度, 即 -0.1 * device.width.
bottom 赋值为 -1, 表示 X 坐标为横向屏幕宽度的代指值, 即 device.width.
ScreenMetricNumberY#
屏幕纵向度量值.
表示方式:
- 数字 { Y >= 1 或 Y < -1 } - 纵向屏幕高度值
- 数字 { Y > -1 且 Y < 1 } - 纵向屏幕高度值的百分比
- 数字 { Y == -1 } - 纵向屏幕高度值本身 (代指值)
例如, 对于下面的参数:
top { ScreenMetricNumberY }
top 赋值为 50, 表示 Y 坐标为 50.
top 赋值为 -80, 表示 Y 坐标为 -80.
top 赋值为 0.5, 表示 Y 坐标为 50% 纵向屏幕高度, 即 0.5 * device.height.
top 赋值为 -0.1, 表示 Y 坐标为 -10% 纵向屏幕高度, 即 -0.1 * device.height.
top 赋值为 -1, 表示 Y 坐标为纵向屏幕高度的代指值, 即 device.height.
ScriptExecuteActivity#
android.app.Activity 的子类.
ScriptExecuteActivity 是 UI 模式下, 全局对象 activity 的类型:
'ui';
activity instanceof org.autojs.autojs.execution.ScriptExecuteActivity; // true
一些 activity 相关的示例:
/* 结束当前 activity. */
activity.finish();
/* 设置状态栏颜色为深红色. */
activity.getWindow().setStatusBarColor(colors.toInt('dark-red'));
/* 将视图对象作为内容加载. */
activity.setContentView(web.newInjectableWebView('www.github.com'));
/* 获取顶层窗口的高度. */
activity.getWindow().getDecorView().getRootView().getHeight();
因 ScriptExecuteActivity 继承了 android.app.Activity 等非常多的 Java 类, 因此 activity 获得了非常丰富的属性和方法, 详情参阅 Android Docs 及 AutoJs6 源码.
DetectCompass#
用于传递给 控件罗盘 的参数类型, 又称 罗盘参数.
罗盘参数是 字符串 类型, 支持单独或组合使用.
下面列举了部分罗盘参数示例:
p- 父控件p2- 二级父控件c0- 索引 0 (首个) 子控件c2- 索引 2 子控件c-1- 末尾子控件s5- 索引 5 兄弟控件s-2- 倒数第 2 兄弟控件s<1- 相邻左侧兄弟节点s>1- 相邻右侧兄弟节点k2- 向上寻找可点击控件 (最多 2 级)p4c0>1>1>0s0- 组合使用
控件罗盘 (UiObject.compass) 是 控件探测 (UiObject.detect) 的衍生方法, 因此类型命名采用了 DetectCompass.
DetectResult#
控件探测 (UiObject.detect) 的结果参数类型, 又称 探测结果, 此过程也称为 结果筛选.
/* 控件. */
detect(w, '#');
detect(w, 'w'); /* 同上. */
detect(w, 'widget'); /* 同上. */
/* 文本内容. */
detect(w, '$');
detect(w, 'txt'); /* 同上. */
detect(w, 'content'); /* 同上. */
/* 点. */
detect(w, '.');
detect(w, 'pt'); /* 同上. */
detect(w, 'point'); /* 同上. */
/* UiObjectInvokable (控件可调用类型). */
detect(w, 'click'); /* i.e. w.click() */
detect(w, [ 'setText', 'hello' ]); /* i.e. w.setText('hello') */
不同于 PickupResult (拾取结果), 探测结果 的种类相对较少.
DetectCallback#
探测回调.
探测回调用于处理 控件探测 (UiObject.detect) 的结果.
回调结果 将影响 探测结果, 当 回调结果 返回 undefined 时, 将直接返回 探测结果, 否则返回 回调结果:
function detect<T extends UiObject, R>(w: T, callback: (w: T) => R): T | R {
let callbackResult: R = callback(w);
return callbackResult == undefined ? w : callbackResult;
}
示例:
let w = pickup(/.+/);
/* 返回 w.content() 的结果. */
detect(w, (w) => w.content());
/* 返回 w 的结果. */
detect(w, (w) => {
console.log(w.content());
});
PickupSelector#
拾取选择器 的 选择器参数.
单一型选择器#
单一型选择器包含 [ 经典选择器 / 内容选择器 / 对象选择器 ].
经典选择器#
text('abc') 或串联形式 text('abc').clickable().centerX(0.5).
内容选择器#
字符串 'abc' 或正则表达式 /abc/.
相当于 content('abc') 及 contentMatch(/abc/).
对象选择器#
将选择器名称作为 键 (key), 选择器参数作为 值 (value).
若参数多于 1 个, 使用数组包含所有参数; 若无参数, 使用 [] (空数组) 或 null, 或默认值 (如 true).
虽然一个参数也可使用数组, 但通常无必要.
/* 经典选择器. */
let selClassic = text('abc').clickable().centerX(0.5).boundsInside(0.2, 0.05, -1, -1).action('CLICK', 'SET_TEXT', 'LONG_CLICK');
/* 对象选择器. */
let selObject = {
text: 'abc',
clickable: [], /* 或 clickable: true . */
centerX: 0.5,
boundsInside: [ 0.2, 0.05, -1, -1 ],
action: [ 'CLICK', 'SET_TEXT', 'LONG_CLICK' ],
};
混合型选择器#
混合型选择器由多个单一型选择器组成.
用数组表示一个混合型选择器, 其中的元素为单一型选择器:
pickup([ /he.+/, clickable(true).boundsInside(0.2, 0.05, -1, -1) ]);
上述示例的选择器参数使用了混合型选择器, 它包含两个单一型选择器, 分别为 内容选择器 和 经典选择器.
上述示例可以转换为单一型选择器:
/* 对象选择器. */
pickup({
contentMatch: /he.+/,
clickable: true,
boundsInside: [ 0.2, 0.05, -1, -1 ],
});
/* 经典选择器. */
pickup(contentMatch(/he.+/).clickable(true).boundsInside(0.2, 0.05, -1, -1));
PickupResult#
拾取选择器 (UiSelector#pickup) 的结果参数类型, 又称 拾取结果, 此过程也称为 结果筛选.
# / w / widget- 控件 (UiObject){} / #{} / {#} / w{} / {w} / wc / collection / list-> 控件集合 (UiObjectCollection)[] / #[] / [#] / w[] / [w] / ws / widgets-> 控件 (UiObject) 数组$ / txt / content- 文本内容 (UiObject#content)$[] / [$] / txt[] / [txt] / content[] / [content] / contents-> 文本内容 (UiObject#content) 数组. / pt / point- 点 (UiObject#point).[] / [.] / point[] / [point] / pt[] / [pt] / points / pts-> 点 (UiObject#point) 数组@ / selector / sel-> 选择器 (UiSelector)? / exists-> 存在判断 (UiSelector#exists)UiObjectInvokable- 控件可调用类型
/* 控件. */
pickup(sel, '#');
pickup(sel, 'w'); /* 同上. */
pickup(sel, 'widget'); /* 同上. */
/* 文本内容. */
pickup(sel, '$');
pickup(sel, 'txt'); /* 同上. */
pickup(sel, 'content'); /* 同上. */
/* 文本内容数组. */
pickup(sel, '$[]');
pickup(sel, 'txt[]'); /* 同上. */
pickup(sel, '[content]'); /* 同上. */
pickup(sel, 'contents'); /* 同上. */
/* 点. */
pickup(sel, '.');
pickup(sel, 'pt'); /* 同上. */
pickup(sel, 'point'); /* 同上. */
/* 点数组. */
pickup(sel, '.[]');
pickup(sel, '[.]'); /* 同上. */
pickup(sel, '[point]'); /* 同上. */
pickup(sel, 'points'); /* 同上. */
/* UiObjectInvokable (控件可调用类型). */
pickup(sel, 'click'); /* i.e. sel.findOnce().click() */
pickup(sel, [ 'setText', 'hello' ]); /* i.e. sel.findOnce().setText('hello') */
与 DetectResult (探测结果) 相比, 拾取结果 的种类更加丰富.
UiObjectInvokable#
控件可调用类型, 用于使用参数形式实现方法调用, 又称 参化调用.
支持所有 UiObject 的实例方法, 如果方法需要传递参数, 需要将参数连同方法名称放入数组后再传递.
/* 无参方法. */
detect(w, 'click'); /* i.e. w.click() */
detect(w, 'imeEnter'); /* i.e. w.imeEnter() */
/* 含参方法. */
detect(w, [ 'child', 0 ]); /* i.e. w.child(0) */
detect(w, [ 'setText', 'hello' ]); /* i.e. w.setText('hello') */
detect(w, [ 'setSelection', 2, 3 ]); /* i.e. w.setSelection(2, 3) */
RootMode#
Root 模式, 枚举类型, 已全局化.
| 枚举实例名 | 描述 | JavaScript 代表参数 |
|---|---|---|
| AUTO_DETECT | 自动检测 Root 权限 | 'auto' / -1 |
| FORCE_ROOT | 强制 Root 模式 | 'root' / 1 / true |
| FORCE_NON_ROOT | 强制非 Root 模式 | 'non-root' / 0 / false |
检测 Root 模式:
console.log(autojs.getRootMode() === RootMode.AUTO_DETECT);
console.log(autojs.getRootMode() === RootMode.FORCE_ROOT);
console.log(autojs.getRootMode() === RootMode.FORCE_NON_ROOT);
设置 Root 模式, 以设置 '强制 Root 模式' 为例:
autojs.setRootMode(RootMode.FORCE_ROOT);
autojs.setRootMode('root'); /* 同上. */
autojs.setRootMode(1); /* 同上. */
autojs.setRootMode(true); /* 同上. */
ColorHex#
颜色代码 (Color Hex Code).
在网页中经常使用的形如 #FF4500 的字符串表示一个颜色.
在 AutoJs6 中, 有三种表示方式, 均使用十六进制代码表示:
#AARRGGBB#
使用四个分量表示颜色, 分量顺序固定为 A (alpha), R (red), G (green), B (blue). 每个分量使用 [0..255] 对应的十六进制数表示, 不足两位时需补零.
例如一个颜色使用 rgba(120, 14, 224, 255) 表示, 将其转换为 #AARRGGBB 格式:
R: 120 -> 0x78
G: 14 -> 0xE
B: 224 -> 0xE0
A: 255 -> 0xFF
#AARRGGBB -> #FF780EE0
注意上述示例的 G 分量需补零.
扩展阅读:
反向转换, 即 '#FF780EE0' 转换为 RGBA 分量:
colors.toRgba('#FF780EE0'); // [ 120, 14, 224, 255 ]获取单独的分量:
let [r, g, b, a] = colors.toRgba('#FF780EE0');
console.log(r); // 120
#RRGGBB#
当 A (alpha) 分量为 255 (0xFF) 时, 可省略 A 分量:
colors.toInt('#CD853F') === colors.toInt('#FFCD853F'); // true
获取 #RRGGBB 的 A (alpha) 分量, 将得到 255:
colors.alpha('#CD853F'); // 255
需额外留意, 当使用十六进制数字表示颜色时, FF 不可省略:
colors.toHex('#CD853F', 8); // #FFCD853F
colors.toHex('#FFCD853F', 8); // #FFCD853F
colors.toHex(0xCD853F); // #00CD853F
colors.toHex(0xFFCD853F); // #FFCD853F
#RGB#
#RRGGBB 十六进制代码的三位数简写形式, 如 #BBFF33 可简写为 #BF3, #FFFFFF 可简写为 #FFF.
与 #RRGGBB 相同, #RGB 的 A (alpha) 分量也恒为 255 (0xFF).
colors.toInt('#BBFF33') === colors.toInt('#BF3'); // true
colors.alpha('#BF3') === 255; // true
ColorInt#
颜色整数 (Color Integer).
多数情况下, 使用颜色整数代表一个颜色.
在安卓源码中, 颜色整数用 ColorInt 表示, 其值的范围由 Java 的 Integer 类型决定, 即 [-2^31..2^31-1].
例如数字 0xBF110523 对应十进制的 3205563683, 超出了上述 ColorInt 的范围, 因此相关方法 (如 colors.toInt) 会将此数值通过 2^32 偏移量移动至合适的范围内, 最终得到结果 -1089403613.
colors.toInt(0xBF110523); // -1089403613
colors.toInt('#BF110523'); /* 结果同上. */
console.log(0xBF110523); // 3205563683
console.log(0xBF110523 - 2 ** 32); // -1089403613
由此可知, 当 ColorInt 作为参数类型传入时, 没有范围限制, 因为参数会通过 2^32 偏移量移动至上述合法范围内. 如 colors.toHex(0xFFFF3300) 将正确返回 "#FF3300", 虽然参数 0xFFFF3300 并不在 [-2^31..2^31-1] 范围内.
当 ColorInt 作为返回值类型时, 其返回值一定位于 [-2^31..2^31-1] 范围内. 如 colors.toInt(0xFFFF3300) 返回 -52480, 此返回值缺乏可读性, 通常只用于作为新的参数传入其他方法.
注:
事实上,-52480是0xFFFF3300 - 2 ** 32的结果.
如需将-52480这样的值还原为具有可读性的颜色代码, 可使用 colors.toHex 等方法.
ColorName#
颜色名称.
颜色列表 (Color Table) 章节中, 各个颜色列表中 "变量名" 的字符串形式可直接作为颜色名称使用:
/* CSS 颜色列表中的 ORANGE_RED. */
/* 作为 ColorInt 使用. */
colors.toHex(colors.css.ORANGE_RED);
/* 作为 ColorName 使用. */
colors.toHex('ORANGE_RED');
/* WEB 颜色列表中的 CREAM. */
/* 作为 ColorInt 使用. */
colors.toHex(colors.web.CREAM);
/* 作为 ColorName 使用. */
colors.toHex('CREAM');
名称冲突#
当使用 颜色名称 (ColorName) 作为参数时, 同一个名称可能同时出现在不同的 颜色列表 中, 如 CYAN 在所有列表中均有出现, 且 Material 颜色列表 中的 CYAN 与其它列表中的 CYAN 颜色不同.
针对上述冲突, 按如下命名空间优先级查找并使用颜色名称对应的颜色:
android > css > web > material
详情参阅 颜色列表 (Color Table) 章节的 颜色名称冲突 小节.
参数格式#
ColorName 除了大写形式 (如 BLACK 或 DARK_RED) 外, 还支持以下几种格式 (以 LIGHT_GREY 为例):
LIGHT_GREY-- 大写 + 下划线LIGHTGREY-- 大写合并light_grey-- 小写 + 下划线lightgrey-- 小写合并light-grey-- 小写 + 连字符
因此下面示例代码的结果是相同的:
colors.toInt(colors.LIGHT_GREY);
colors.toInt('LIGHT_GREY');
colors.toInt('LIGHTGREY');
colors.toInt('light_grey');
colors.toInt('lightgrey');
colors.toInt('light-grey');
ColorComponent#
颜色分量类型.
例如表示一个值为 128 的 R (red) 分量, 可使用 128, 0.5 及 50% 等表示法.
分量表示法#
通常使用整数表示一个颜色分量, 如 colors.rgb(10, 20, 30).
RGB 系列色彩模式范围为 [0..255], HSX 系列色彩模式范围为 [0..100].
除上述整数分量表示法, AutoJs6 还支持百分数等方式表示一个颜色分量 (如 0.2, "20%" 等).
下表列举了 AutoJs6 支持的分量表示法:
1. 整数
| 样例 | 等效语句 | 备注 |
|---|---|---|
| colors.rgb(64, 32, 224) | - | - |
| colors.rgba(64, 32, 224, 255) | - | - |
| colors.hsv(30, 20, 60) | colors.hsv(30, 0.2, 0.6) | S (saturation) 和 V (value) 分量范围为 [0..100] |
| colors.hsva(30, 20, 60, 255) | colors.hsva(30, 0.2, 0.6, 255) | A (alpha) 分量范围为 [0..255] |
2. 浮点数
| 样例 | 等效语句 | 备注 |
|---|---|---|
| colors.rgb(0.5, 0.25, 0.125) | colors.rgb(128, 64, 32) | - |
| colors.rgba(0.5, 0.25, 0.1, 0.2) | colors.rgba(128, 64, 26, 51) | - |
| colors.hsv(10, 0.3, 0.2) | colors.hsv(10, 30, 20) | - |
| colors.hsva(10, 0.3, 0.2, 0.5) | colors.hsva(10, 30, 20, 128) | 不同分量的范围不同 |
3. 百分数
| 样例 | 等效语句 | 备注 |
|---|---|---|
| colors.rgb('50%', '25%', '12.5%') | colors.rgb(128, 64, 32) | - |
| colors.rgba('50%', '25%', '10%', '20%') | colors.rgba(128, 64, 26, 51) | - |
| colors.hsv(10, '30%', '20%') | colors.hsv(10, 30, 20) | - |
| colors.hsva(10, '30%', '20%', '50%') | colors.hsva(10, 30, 20, 128) | 不同分量的范围不同 |
表示范围#
不同分量的范围不同, 当使用浮点数或百分数等表示法时, 需留意其表示范围:
| 分量 | 范围 |
|---|---|
| R (red) | [0..255] |
| G (green) | [0..255] |
| B (blue) | [0..255] |
| A (alpha) | [0..255] |
| H (hue) | [0..360] |
| S (saturation) | [0..100] |
| V (value) | [0..100] |
| L (lightness) | [0..100] |
colors.hsva(0.5, 0.5, 0.5, 0.5);
colors.hsva(180, 50, 50, 128); /* 同上. */
表示法组合#
分量表示法支持组合使用:
colors.rgb(0.5, '25%', 32); /* 相当于 colors.rgb(128, 64, 32) . */
colors.rgba(0.5, '25%', 32, '50%'); /* 相当于 colors.rgba(128, 64, 32, 128) . */
灵活的 1#
在组合使用分量表示法时, 1 既可作为整数分量也可作为百分数分量, 原则如下:
对于非 RGB 分量, 如 A (alpha), S (saturation), V (value), L (lightness) 等, 1 一律解释为 100%.
colors.argb(1, 255, 255, 255); /* 相当于 argb(255, 255, 255, 255), 1 解释为 100% . */
colors.hsv(60, 1, 0.5); /* S 分量相当于 100, 1 解释为 100% . */
colors.hsla(0, 1, 1, 1); /* 相当于 hsla(0, 100, 100, 255) . */
而对于 RGB 分量, 只有当 R / G / B 三个分量全部满足 c <= 1 且不全为 1 时, 解释为百分数 1 (即 100%), 其他情况, 解释为整数 1.
colors.rgb(1, 0.2, 0.5); /* 相当于 rgb(255, 51, 128), 1 解释为 100%, 得到 255 . */
colors.rgb(1, 0.2, 224); /* 相当于 rgb(1, 51, 224), 1 解释为 1 . */
colors.rgb(1, 160, 224); /* 无特殊转换, 1 解释为 1 . */
colors.rgb(1, 1, 1); /* 相当于 rgb(1, 1, 1), 颜色代码为 #010101, 1 全部解释为 1 . */
colors.rgb(1, 1, 0.5); /* 相当于 rgb(255, 255, 128), 1 全部解释为 100% . */
由此可见, 对于 RGB 分量, 只要有一个分量使用了 0.x 的百分数表示法, 1 将全部解释为 255 (100%).
1 与 1.0#
JavaScript 只有数字类型, 1 与 1.0 没有区别, 以下两个语句完全等价:
colors.rgb(1, 1, 0.5);
colors.rgb(1.0, 1.0, 0.5); /* 同上. */
因此当使用 1 表示 100% 传入一个颜色分量参数时, 建议使用 1.0 以增加可读性:
colors.hsla(120, 0.32, 1.0, 0.5); /* 使用 1.0 代表 100% . */
ColorComponents#
颜色分量 数组.
同一种颜色可用不同的色彩模式表示, 如 RGB 色彩模式或 HSV 色彩模式等.
每个色彩模式的 分量 (Component) 组成的数组称为颜色分量数组, 如 RGB 色彩模式的分量数组 [100, 240, 72] 表示 R (red) 分量为 100, G (green) 分量为 240, B (blue) 分量为 72, 访问时可使用数组下标方式或解构赋值方式:
let components = colors.toRgb(colors.rgb(100, 240, 72)); // [ 100, 240, 72 ]
/* 数组下标方式. */
console.log(`R: ${components[0]}, G: ${components[1]}, B: ${components[2]}`);
/* 结构赋值方式. */
let [ r, g, b ] = components;
console.log(`R: ${r}, G: ${g}, B: ${b}`);
colors 全局对象的很多 "to" 开头的方法都可返回颜色分量数组, 如 toRgb, toHsv, toHsl, toRgba, toArgb 等.
需额外注意 toRgba 和 toArgb 结果中的 A (alpha) 分量, 默认范围为 [0..255], 而其他方法则恒为 [0..1]:
colors.toRgba('blue-grey')[3]; /* A 分量为 255. */
colors.toArgb('blue-grey')[0]; /* A 分量为 255. */
colors.toHsva('blue-grey')[3]; /* A 分量为 1. */
colors.toHsla('blue-grey')[3]; /* A 分量为 1. */
如需使 toRgba 和 toArgb 结果中 A (alpha) 分量范围也为 [0..1], 可使用 maxAlpha 参数:
colors.toRgba('blue-grey', { maxAlpha: 1 })[3]; /* A 分量为 1. */
ColorDetectionAlgorithm#
颜色检测算法, 用于检测两个颜色之间的差异程度, 即颜色差异.
颜色差异 (Color Difference), 也称为颜色距离, 是色彩学领域的一个参量.
颜色差异将一个抽象概念进行了量化, 例如可以通过色彩空间内的 欧氏距离 (Euclidean Distance) 计算出一个具体的差异量.
量化颜色差异时, 存在多种不同的量化方法, 通常使用颜色检测算法计算欧式距离, 由此距离进行颜色差异的量化.
AutoJs6 内置了几种不同的颜色检测算法, 这些算法通常作为参数传入到某个函数中.
RGB 差值检测#
参数名称: diff
计算两个 RGB 颜色各分量的差值:
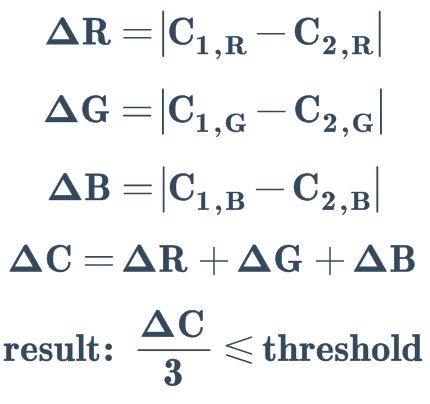
RGB 距离检测#
参数名称: rgb
计算 RGB 色彩空间中两点间距离:
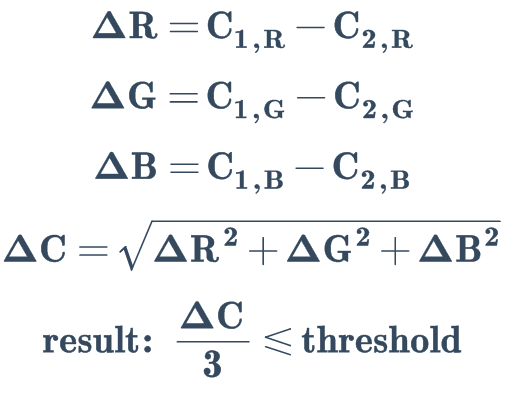
加权 RGB 距离检测#
参数名称: rgb+
带有权重的 RGB 距离检测 (Delta E):
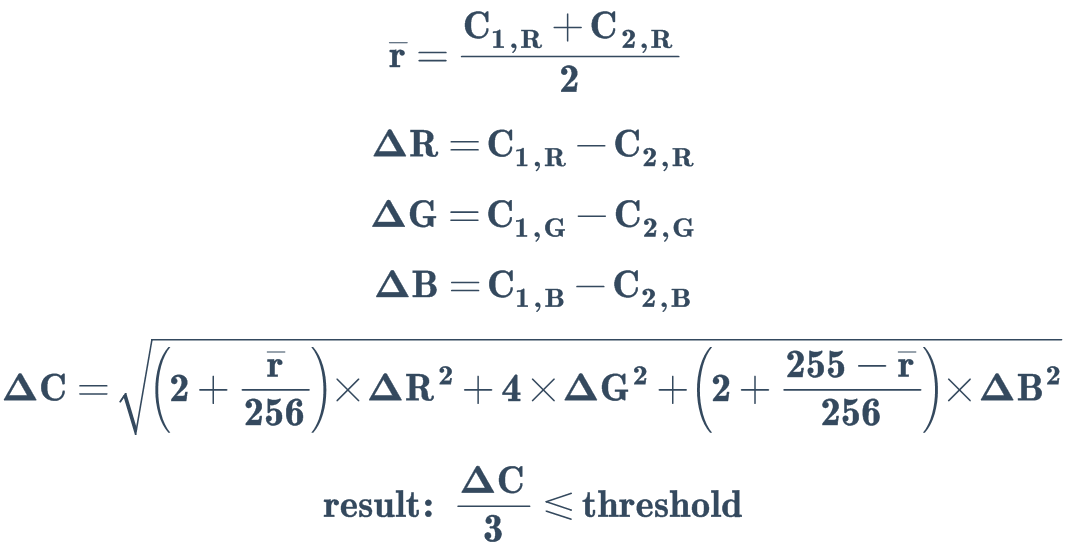
参阅:
Colour metric (from compuphase.com)
CIELAB Delta E* (from Wikipedia)
H 距离检测#
参数名称: h
HSV 色彩空间中 H (hue) 分量的距离检测:
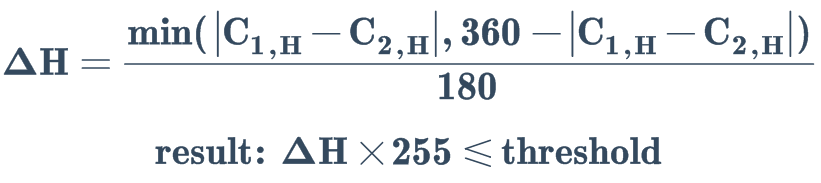
HS 距离检测#
参数名称: hs
HSV 色彩空间中 H (hue) 及 S (saturation) 的相关距离检测:
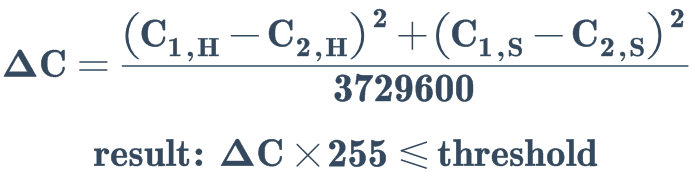
Range#
表示一个数字的数值范围.
| 表示法 | 范围 |
|---|---|
| (a..b) | { x | a < x < b } |
| [a..b] | { x | a <= x <= b } |
| (a..b] | { x | a < x <= b } |
| [a..b) | { x | a <= x < b } |
| (a..+∞) | { x | x > a } |
| [a..+∞) | { x | x >= a } |
| (-∞..b) | { x | x < b } |
| (-∞..b] | { x | x <= b } |
| (-∞..+∞) | { x } (任意值) |
如 Range[10..30] 表示数字 x 位于 10 <= x <= 30 范围内, 而 Range[0..1) 表示数字 x 位于 0 <= x < 1 范围内.
IntRange#
表示一个整数的取值范围. 其表示法可参阅 Range 小节.
如 IntRange[10..30] 表示整数 x 位于 10 <= x <= 30 范围内, 而 IntRange[0..100) 表示整数 x 位于 0 <= x < 100 范围内.
StandardCharset#
StandardCharset 类型支持 Java 字符集 (Charset 类) 形式及字符串形式:
| Charset | String | Wikipedia |
|---|---|---|
| ISO_8859_1 | "ISO_8859_1" / "iso-8859-1" | 英 / 中 |
| US_ASCII | "US_ASCII" / "us-ascii" | 英 / 中 |
| UTF_8 | "UTF_8" / "utf-8" | 英 / 中 |
| UTF_16 | "UTF_16" / "utf-16" | 英 / 中 |
| UTF_16BE | "UTF_16BE" / "utf-16be" | 英 |
| UTF_16LE | "UTF_16LE" / "utf-16le" | 英 |
Charset 类可由 StandardCharsets 的静态常量获取, 如 StandardCharsets.UTF_8.
字符串表示 StandardCharset 类型时, 支持与上述静态常量同名的大写形式, 如 'UTF_8', 以及带连字符的小写形式, 如 'utf-8'.
Typescript declaration (TS 声明):
declare type StandardCharset = java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets
| 'US_ASCII' | 'ISO_8859_1' | 'UTF_8' | 'UTF_16BE' | 'UTF_16LE' | 'UTF_16'
| 'us-ascii' | 'iso-8859-1' | 'utf-8' | 'utf-16be' | 'utf-16le' | 'utf-16';
JavaScript 实例:
/**
* @param {StandardCharset} char
* @returns void
*/
function test(char) {
/* ... */
}
test(StandardCharsets.UTF_8); /* Charset 类形式. */
test('UTF_8'); /* 字符串大写形式. */
test('utf-8'); /* 字符串小写形式. */
注: 在 AutoJs6 中, StandardCharsets 支持全局化调用.
参阅: Oracle Docs
ExtendModulesNames#
AutoJs6 内置扩展插件 的插件名称.
支持的字符串常量:
'Arrayx'' 或'Array''Numberx'' 或'Number''Mathx'' 或'Math'
/* 启用 Array 内置扩展插件. */
plugins.extend('Arrayx');
plugins.extend('Arrayx'); /* 同上. */
ActivityShortForm#
AutoJs6 跳转内部 Activity 的页面简称.
这些简称全部对应于 AutoJs6 内置的 Activity 页面, 如 AutoJs6 的日志页面和设置页面等.
/* 跳转至 AutoJs6 日志页面. */
app.startActivity('console');
app.startActivity('log'); /* 同上. */
/* 跳转至 AutoJs6 主页页面. */
app.startActivity('homepage');
app.startActivity('home'); /* 同上. */
支持的全部页面简称:
- 日志页面 -
console/log - 设置页面 -
settings/preferences/pref - 主页页面 -
homepage/home - 关于页面 -
about - 打包页面 -
build - 文档页面 -
documentation/doc/docs
BroadcastShortForm#
AutoJs6 可接收的广播行为简称.
这些简称全部对应于 AutoJs6 可接收的广播行为, 如进行布局范围分析等.
/* 发送 "布局范围分析" 广播. */
app.sendBroadcast('inspect_layout_bounds');
app.sendBroadcast('layout_bounds'); /* 同上. */
app.sendBroadcast('bounds'); /* 同上. */
/* 发送 "布局层次分析" 广播. */
app.sendBroadcast('inspect_layout_hierarchy');
app.sendBroadcast('layout_hierarchy');
app.sendBroadcast('hierarchy'); /* 同上. */
支持的全部广播行为简称:
- 布局范围分析 -
inspect_layout_bounds/layout_bounds/bounds - 布局层次分析 -
inspect_layout_hierarchy/layout_hierarchy/hierarchy
OcrModeName#
AutoJs6 的 OCR 模式名称.
当使用不同的模式名称时, ocr 全局方法及其相关方法 (如 ocr.detect) 将使用不同的引擎, 进而可能获得不同的识别速度和结果.
mlkit- 代表 MLKit 引擎paddle- 代表 Paddle Lite 引擎
OcrResult#
OcrResult 是一个代表 OCR 识别结果的接口.
OcrResult
[p] label#
- { string }
OCR 识别结果的文本标签, 通常可用于最终的文字识别结果.
images.requestScreenCapture();
let img = images.captureScreen();
let results = ocr.detect(img);
results.map(o => o.label); /* 将识别结果全部映射为文本标签. */
[p] confidence#
- { string }
OCR 识别结果的置信度, 置信度越高, 意味着识别结果可能越准确.
images.requestScreenCapture();
let img = images.captureScreen();
let results = ocr.detect(img);
results.filter(o => o.confidence > 0.9); /* 筛选置信度高于 0.9 的结果. */
[p] bounds#
- { AndroidRect }
OCR 识别结果的位置矩形, 用 AndroidRect 表示.
images.requestScreenCapture();
let img = images.captureScreen();
let results = ocr.detect(img);
let clickToStart = results.find(o => o.label === '点击开始');
if (!isNullish(clickToStart)) {
/* 点击 OCR 识别结果的位置矩形. */
click(clickToStart.bounds);
}
[m] toString#
toString()#
- returns { string }
OCR 识别结果的 toString 覆写方法, 格式示例:
OcrResult@46a77f4{label=19:43:52, confidence=0.9165039, bounds=Rect(14, 15 - 121, 35)}
OcrResult@9fed472{label=Service, confidence=0.88002235, bounds=Rect(30, 76 - 106, 97)}
OcrResult@59cab38{label=Tools, confidence=0.8421875, bounds=Rect(30, 324 - 88, 345)}
ThemeColor#
AutoJs6 内置类 org.autojs.autojs.theme.ThemeColor 的别名.
ThemeColor 表示一个主题颜色.
常见相关方法或属性:
- autojs.themeColor
- Color(themeColor)
当 ThemeColor 作为 OmniColor 使用时, 将使用其 "主色" 作为色值:
let themeColor = autojs.themeColor;
Color(themeColor).toInt() === Color(themeColor.getColorPrimary()).toInt(); // true
JsByteArray#
JavaScript 用于表示 "字节数组" 的类型, 即 number[].
注: Java 使用 byte[] 类型表示字节数组.
将 JavaScript 字节数组转换为 JavaScript 字符串:
let arr = [ 104, 101, 108, 108, 111 ];
let string = ArrayUtils.jsBytesToString(arr);
console.log(string); // hello
将 JavaScript 字符串转换为 Java 字节数组:
let str = 'hello';
let bytes = new java.lang.String(str).getBytes();
console.log(bytes); // [ 104, 101, 108, 108, 111 ]
console.log(species(bytes)); // JavaArray
将 JavaScript 字节数组转换为 Java 字节数组:
let arr = [ 104, 101, 108, 108, 111 ];
let bytes = ArrayUtils.jsBytesToByteArray(arr);
console.log(bytes); // [ 104, 101, 108, 108, 111 ]
console.log(species(bytes)); // JavaArray
ByteArray#
Java 用于表示 "字节数组" 的类型, 即 byte[].
注: Kotlin 使用 ByteArray 类型表示字节数组.
Java 字节数组不是 JavaScript 的 number[]:
console.log(util.getClass(new java.lang.String('hello').getBytes())); // class [B
console.log(util.getClassName(new java.lang.String('hello').getBytes())); // [B
Java 字节数组转换为 JavaScript 字符串:
let bytes = new java.lang.String('hello').getBytes();
console.log(bytes); // [ 104, 101, 108, 108, 111 ]
let str = String(new java.lang.String(bytes));
console.log(str); // hello
在 Java 中, 字节数组中的元素范围为 [-127..128]:
let key = new crypto.Key('a'.repeat(16));
console.log(
crypto.encrypt('hello world', key, 'AES')
); // [ 105, -52, -100, 42, -7, 27, -87, -32, 83, -59, 25, 115, -103, -75, 98, 18 ]
如需转换为 [0..255] 范围, 可使用 x & 0xFF 的转换方式:
let key = new crypto.Key('a'.repeat(16));
console.log(
crypto.encrypt('hello world', key, 'AES').map(x => x & 0xFF)
); // [ 105, 204, 156, 42, 249, 27, 169, 224, 83, 197, 25, 115, 153, 181, 98, 18 ]
CryptoDigestAlgorithm#
密文 模块使用的消息摘要算法.
| 值 (字符串) |
|---|
| MD5 |
| SHA-1 |
| SHA-224 |
| SHA-256 |
| SHA-384 |
| SHA-512 |
MD: 消息摘要算法 (Message-Digest algorithm), 其中 MD5 被广泛使用. MD5 是一种密码散列函数, 可生成一个 128 位散列值 (常表示为 32 位十六进制数字), 以确保信息传输完整一致.
SHA: 安全散列算法 (Secure Hash Algorithm), 一个密码散列函数家族. 可计算出消息对应的长度固定的字符串 (即消息摘要) 的算法. 输入消息不同, 消息摘要有很高的概率会不同. 当不同消息得到相同的消息摘要 (即使概率很低) 时, 称为散列碰撞或哈希冲突.
/* 获取字符串 "hello" 的 MD5 摘要. */
console.log(crypto.digest('hello', 'MD5')); // 5d41402abc4b2a76b9719d911017c592
/* 获取字符串 "hello" 的 SHA-1 摘要. */
console.log(crypto.digest('hello', 'SHA-1')); // aaf4c61ddcc5e8a2dabede0f3b482cd9aea9434d
/* 空文 MD5. */
console.log(crypto.digest('', 'MD5')); // d41d8cd98f00b204e9800998ecf8427e
参阅: Oracle Docs / 常用消息摘要算法简介
CryptoKeyPairGeneratorAlgorithm#
密文 模块使用的密钥对生成器算法.
| 值 (字符串) | 别名 |
|---|---|
| DH | DiffieHellman |
| DSA | - |
| RSA | - |
| EC | - |
| XDH | - |
例如, AutoJs6 的 crypto.generateKeyPair 方法可以生成用于非对称加密算法的公私密钥对:
let kp = crypto.generateKeyPair('DSA', 1024);
console.log(kp.publicKey);
console.log(kp.privateKey);
上述示例的 'DSA' 即为有效的密钥对生成器算法之一.
参阅: Oracle Docs
CryptoDigestOptions#
消息摘要生成选项, 主要用于 密文 模块.
| 属性 | 有效值 | 简述 |
|---|---|---|
| input | 'file' / 'base64' / 'hex' / 'string' | 指定输入类型. |
| output | 'bytes' / 'base64' / 'hex' / 'string' | 指定输出类型. |
| encoding | 'US-ASCII' / 'ISO-8859-1' / 'UTF-8' 'UTF-16BE' / 'UTF-16LE' / 'UTF-16' |
指定输入或输出编码, 仅对 'string' 类型有效. |
注: 上表中粗体值为属性默认值.
CryptoCipherTransformation#
密码转换名称, 主要用于 密文 模块.
Cipher, 可翻译为 "密码" 或 "密码器".
AutoJs6 的 crypto 模块中, encrypt 和 decrypt 的内部实现均借助了 javax.crypto.Cipher 实例.
javax.crypto.Cipher 类提供加解密功能, 它构成了 JCE (Java Cryptography Extension) 的核心, 是 Java JDK 原生 API.
Cipher 实例的初始化使用的是 Cipher.getInstance(transformation: String) 方法, 这个 transformation 参数, 即 "转换名称", 其作用就是获取到不同加解密方式的 Cipher 实例.
转换名称 transformation 参数的格式有两种:
- 算法名称 (algorithm)
- 算法名称/工作模式/填充方式 (algorithm/mode/padding)
/* 转换名称格式为 "算法名称" 的 Cipher 实例. */
let cipherA = Cipher.getInstance("AES");
/* 转换名称格式为 "算法名称/工作模式/填充方式" 的 Cipher 实例. */
let cipherB = Cipher.getInstance("DES/CBC/PKCS5Padding");
常见相关方法或属性:
- crypto.encrypt(data, key, transformation, options?)
- crypto.decrypt(data, key, transformation, options?)
下表列出了 AutoJs6 支持的转换名称构成要素, 可组合出多种不同的转换名称:
| 算法名称 | 工作模式 | 填充方式 |
|---|---|---|
| AES | CBC CFB CTR CTS ECB OFB |
ISO10126Padding NoPadding PKCS5Padding |
| AES | GCM | NoPadding |
| AES_128 | CBC ECB |
NoPadding PKCS5Padding |
| AES_128 | GCM | NoPadding |
| AES_256 | CBC ECB |
NoPadding PKCS5Padding |
| AES_256 | GCM | NoPadding |
| ARC4 | ECB | NoPadding |
| ARC4 | NONE | NoPadding |
| BLOWFISH | CBC CFB CTR CTS ECB OFB |
ISO10126Padding NoPadding PKCS5Padding |
| ChaCha20 | NONE Poly1305 |
NoPadding |
| DES | CBC CFB CTR CTS ECB OFB |
ISO10126Padding NoPadding PKCS5Padding |
| DESede | CBC CFB CTR CTS ECB OFB |
ISO10126Padding NoPadding PKCS5Padding |
| RSA | ECB NONE |
NoPadding OAEPPadding PKCS1Padding OAEPwithSHA-1andMGF1Padding OAEPwithSHA-224andMGF1Padding OAEPwithSHA-256andMGF1Padding OAEPwithSHA-384andMGF1Padding OAEPwithSHA-512andMGF1Padding |
以 DES 算法为例, 以下均为有效的转换名称:
- DES
- DES/CBC/ISO10126Padding
- DES/CBC/PKCS5Padding
- DES/ECB/PKCS5Padding
- DES/ECB/NoPadding
- ... ...
Storage#
参阅 Storage - 存储类 类型章节.
AndroidBundle#
参阅 AndroidBundle 类型章节.
AndroidRect#
参阅 AndroidRect 类型章节.
CryptoCipherOptions#
参阅 CryptoCipherOptions 类型章节.
ConsoleBuildOptions#
参阅 ConsoleBuildOptions 类型章节.
HttpRequestBuilderOptions#
参阅 HttpRequestBuilderOptions 类型章节.
HttpRequestHeaders#
参阅 HttpRequestHeaders 类型章节.
HttpResponseBody#
参阅 HttpResponseBody 类型章节.
HttpResponseHeaders#
参阅 HttpResponseHeaders 类型章节.
HttpResponse#
参阅 HttpResponse 类型章节.
InjectableWebClient#
参阅 InjectableWebClient 类型章节.
InjectableWebView#
参阅 InjectableWebView 类型章节.
NoticeOptions#
参阅 NoticeOptions 类型章节.
NoticeChannelOptions#
参阅 NoticeChannelOptions 类型章节.
NoticePresetConfiguration#
参阅 NoticePresetConfiguration 类型章节.
NoticeBuilder#
参阅 NoticeBuilder 类型章节.
Okhttp3HttpUrl#
参阅 Okhttp3HttpUrl 类型章节.
OcrOptions#
参阅 OcrOptions 类型章节.
Okhttp3Request#
参阅 Okhttp3Request 类型章节.
OpenCVPoint#
参阅 OpenCVPoint 类型章节.
OpenCVRect#
参阅 OpenCVRect 类型章节.
OpenCVSize#
参阅 OpenCVSize 类型章节.
OpenCCConversion#
参阅 OpenCCConversion 类型章节.